Introduction:
Power banks have become essential for individuals and businesses alike, providing portable and reliable power for devices when traditional charging options aren’t available. However, a power bank is more than just a simple battery; it’s a complex system composed of various components that work together to ensure safe and efficient charging.
Understanding the key components of a power bank is crucial for wholesalers, brands, and B2B customers, as it allows for better product selection, quality control, and marketing strategies.
What Are the Main Components of a Power Bank?
A power bank consists of several key components, including battery cells, charging circuits, protection circuits, input/output ports, LED indicators, and casing.
Each part plays a vital role in the overall functionality, safety, and efficiency of the device.
Understanding these components can help businesses choose the best power bank models to offer their customers.
Battery Cells
The battery cells are the heart of any power bank. There are typically two types of battery cells used in power banks:
- Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) Cells: These are the most commonly used battery cells due to their high energy density, relatively low cost, and long life cycle. However, they are sensitive to overcharging and high temperatures, requiring proper protection circuits.
- Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) Cells: Li-Po cells are newer technology, offering greater flexibility in design as they can be shaped to fit smaller or thinner devices. They are generally safer than Li-Ion cells but tend to be more expensive.
For businesses, understanding the differences between these two types of cells can help in selecting the right models based on budget, performance, and safety requirements.
Charging Circuit
The charging circuit controls how power is transferred from the power bank to the device being charged. This component is responsible for regulating the voltage and current, ensuring that the correct amount of power is delivered to the device.
The charging circuit also manages the recharging process for the power bank itself, converting input power to a usable form for the internal battery cells.
- Voltage Regulation: Ensures a stable output voltage to protect connected devices.
- Current Control: Limits the current to prevent overcharging and overheating, protecting both the power bank and the device.
For B2B customers, a well-designed charging circuit is essential to ensure product reliability and avoid returns due to faulty charging issues.
Protection Circuit
Safety is paramount in any power bank, and this is where the protection circuit comes into play. The protection circuit guards against common electrical issues such as:
- Overcharge Protection: Prevents the battery from being overcharged, which can lead to reduced battery life or even overheating and fire hazards.
- Over-discharge Protection: Stops the battery from discharging below a certain voltage, which can damage the battery cells.
- Short Circuit Protection: Detects and cuts off power in the event of a short circuit, preventing damage to the device or the power bank itself.
- Overcurrent Protection: Ensures that the current drawn from the power bank does not exceed safe levels, protecting both the battery cells and the connected device.
For wholesalers and brands, offering power banks with strong protection circuits is crucial to meet safety standards and build customer trust.
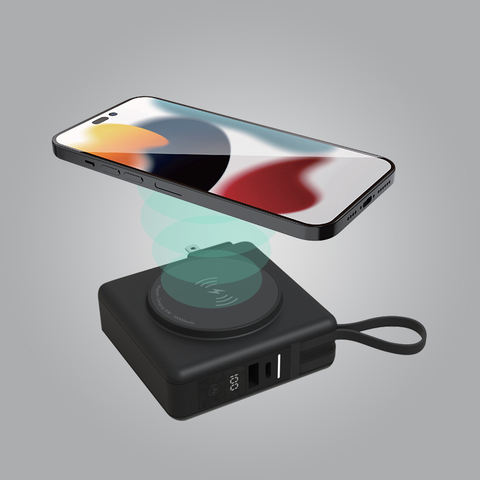
Input/Output Ports
The ports on a power bank are the connection points for charging the device and recharging the power bank itself. Common types of ports include:
- USB-A: The traditional and most widely used port for output.
- USB-C: A newer, faster port that supports both input and output, making it ideal for charging modern smartphones, laptops, and other devices.
- Micro-USB: Often used as the input port to recharge the power bank.
- Lightning Port: Some power banks include a Lightning port specifically for Apple devices.
For B2B customers, the type and number of ports are important considerations, as they determine the power bank’s compatibility with various devices and how many devices can be charged simultaneously.
LED Indicators
LED indicators provide a visual representation of the power bank’s charge status. Typically, power banks feature a series of small LED lights that show the remaining battery capacity and whether the device is charging or discharging.
- Battery Level: Most power banks use a 4-5 LED system to indicate the remaining charge, with each light representing approximately 25% of the total battery capacity.
- Charging Status: Some power banks include a special LED indicator to show when the power bank is actively charging or discharging.
For businesses, the inclusion of clear, easy-to-read indicators can enhance the user experience and reduce customer confusion or dissatisfaction.
Casing
The casing of a power bank serves two primary purposes: protection and aesthetics. The casing must protect the internal components from external damage, such as drops or impacts, while also providing a design that appeals to consumers.
- Material: Power bank casings are typically made from plastic, aluminum, or a combination of materials. Metal cases are more durable and offer better heat dissipation, while plastic cases tend to be lighter and more cost-effective.
- Design: For brands, the design and material of the casing are key differentiators in the market. Sleek, stylish designs can make a product more appealing, especially to premium customers.
For wholesalers and brands, selecting power banks with durable and visually appealing casings can increase customer satisfaction and reduce returns due to damage.
Summary:
Understanding the components of a power bank is essential for any business involved in the manufacturing, wholesale, or retail of these devices. Each component—from the battery cells to the protection circuits—plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and overall performance of the power bank.
For B2B customers, selecting power banks with high-quality components can enhance brand reputation, reduce returns, and meet the evolving demands of consumers.
When choosing power banks to offer to your customers, it’s important to prioritize safety features, charging efficiency, and durable design, ensuring your product stands out in a competitive market.