Power banks have become indispensable in today’s fast-paced world. But alongside their convenience comes the responsibility of ensuring they are safe to use. For manufacturers, integrating robust safety features is critical not only for user protection but also for brand reputation. This guide dives deep into the essential safety features every power bank should have and offers comprehensive safety tips for users.
What Are the Risks of Power Banks?
Overheating
Power banks can generate excessive heat, especially during fast charging or high usage. Overheating not only reduces battery efficiency but can also lead to battery failure or, in extreme cases, explosions. This risk is heightened when devices are charged in high-temperature environments, such as inside cars or under direct sunlight.
Short Circuits
Short circuits occur when there’s an unintended connection between the positive and negative terminals of the battery. This can result from using damaged cables or ports, leading to sparks, fires, or even explosions.
Overcharging or Over-discharging
While modern batteries are designed to handle multiple charge cycles, excessive charging or discharging can degrade their performance. Overcharging can cause swelling of lithium-ion batteries, while over-discharging might lead to irreversible damage.
Explosions
While rare, explosions in power banks are often caused by substandard batteries, defective circuits, or mishandling. These risks underscore the importance of choosing high-quality components during manufacturing.

Essential Safety Features Every Power Bank Must Have
Integrating cutting-edge safety features is crucial for power bank manufacturers. Let’s explore these features in detail:
1. Overcharge Protection
This feature prevents the power bank’s battery from receiving excessive charge, which can cause overheating or damage. It ensures the battery stops charging once it reaches full capacity. Advanced designs use a monitoring chip to regulate the charging cycle.
Why It Matters: Overcharge protection extends the lifespan of the battery and safeguards user devices from potential damage.
2. Short-Circuit Protection
Short-circuit protection automatically shuts off the power supply when a short is detected. This feature uses internal safety mechanisms like fuses or circuit breakers to halt electricity flow and prevent damage to the power bank and connected devices.
Why It Matters: Short-circuit protection is critical for preventing dangerous sparks or electrical fires.
3. Over-temperature Protection
This feature regulates heat generated within the power bank during charging and discharging. By monitoring the internal temperature, it automatically reduces power output or halts the charging process if excessive heat is detected.
Why It Matters: Protects both the user and the power bank from overheating, reducing the risk of explosions or malfunctions.
4. Over-current and Over-voltage Protection
These protections ensure that the power bank delivers a steady, safe flow of electricity to connected devices. Over-current protection limits the amount of current output, while over-voltage protection prevents sudden voltage spikes.
Why It Matters: Shields user devices from being fried due to voltage irregularities, protecting expensive gadgets.
5. Auto Shutoff
This feature ensures that the power bank powers down after a period of inactivity or once the device it’s charging is fully charged. It’s an energy-saving feature that also prevents unnecessary battery drain.
Why It Matters: Conserves battery life and ensures the device operates efficiently during its lifespan.
How to Use a Power Bank Safely
Even the best-designed power banks can become hazardous if not used properly. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure safe operation:
Use High-Quality Cables
Always use certified, high-quality cables to avoid issues like overheating or slow charging. Cheap cables may have substandard insulation or wiring that increases the risk of electrical fires.
Keep Ports Clean
Dust and debris can accumulate in USB ports, interfering with charging and potentially causing shorts. Regularly inspect and clean the ports with a soft, dry cloth or a can of compressed air.
Avoid Extreme Temperatures
Power banks operate optimally within specific temperature ranges (typically 0°C–45°C). Avoid exposing them to direct sunlight, freezing temperatures, or excessive heat to prevent damage.
Don’t Overcharge or Leave Unattended
While many power banks include overcharge protection, it’s still a good practice to unplug them once fully charged. Prolonged charging can stress the battery, especially in older models.
Inspect for Damage
If you notice swelling, leaks, or unusual heat during charging, discontinue use immediately. Damaged batteries can be highly volatile and should be handled carefully.
Can Power Banks Be Left Charging Overnight? (Myth vs. Reality)
This is a common question, and the answer largely depends on the power bank’s design and quality.
The Reality
Modern power banks with lithium-ion batteries and advanced safety features, such as overcharge protection and auto shutoff, are safe to leave charging overnight. However, this safety is not universal. Low-quality or counterfeit power banks may lack these safeguards, increasing the risk of overheating or damage.
Pro Tip: Even with high-quality models, it’s best to charge during the day and place the power bank on a heat-resistant surface while charging to minimize risks.
Precautions to Avoid Power Bank Hazards
Here are additional precautions manufacturers can recommend to their customers:
Choose Reputable Brands
Advise users to purchase power banks from trusted brands that meet international safety standards, such as CE, FCC, and RoHS certifications. This ensures compliance with safety regulations.
Avoid Overloading Power Banks
Using a power bank to charge multiple devices simultaneously may strain its components. Encourage users to check the maximum output specifications before connecting multiple devices.
Air Travel Guidelines
Remind users to carry power banks in their hand luggage instead of checked baggage due to airline safety regulations. Many airlines have restrictions on capacity limits (e.g., less than 100Wh for carry-on).
Proper Storage
Power banks should be stored in a cool, dry place when not in use. Prolonged exposure to moisture or extreme temperatures can degrade the battery and internal circuitry.
Dispose of Responsibly
Old or damaged power banks should never be thrown in regular trash. Encourage customers to dispose of them at e-waste recycling facilities.

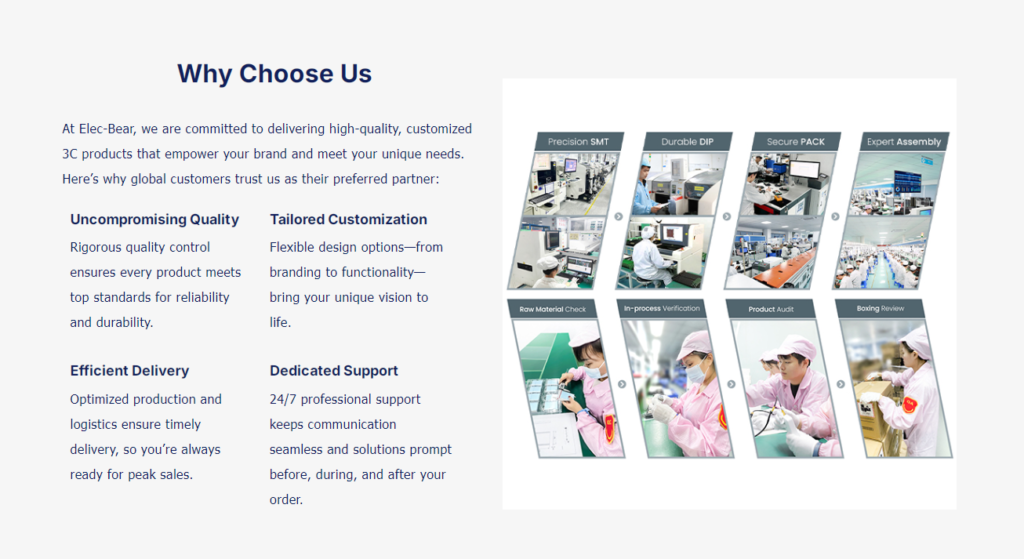
Why Choose Our Power Banks?
At Elec-bear, we pride ourselves on offering customizable, high-quality power banks with a focus on safety and innovation. Whether you’re a brand looking to enhance your product portfolio or a business seeking promotional products, our power banks deliver:
- Superior Safety Standards: Certified by CE, FCC, and RoHS.
- Custom Branding Options: Stand out with unique designs and your logo.
- Long-Lasting Performance: Equipped with high-capacity batteries for extended use.
- Eco-Friendly Solutions: Compliant with environmental safety standards.
Conclusion
Safety is the cornerstone of every reliable power bank. By incorporating advanced safety features like overcharge and short-circuit protection, along with educating users about precautions, manufacturers can ensure customer satisfaction and brand trust. As the power bank market continues to grow, investing in robust safety technologies will be the defining factor for successful brands.